Potassium feldspar is generally flesh-red, yellow-white, white, or gray; the crystals are often short columnar or thick plate-shaped; glass luster; specific gravity 2.56; Mohs hardness 6; melting point 1290℃. It is mainly used for glass and ceramics, and can also be used to make potash fertilizer.
Potassium feldspar ores in nature usually contain a variety of impurities, such as quartz, mica, rutile, magnetite, etc., and magnetic separation, flotation, and other processes are often used to remove impurities during ore dressing.
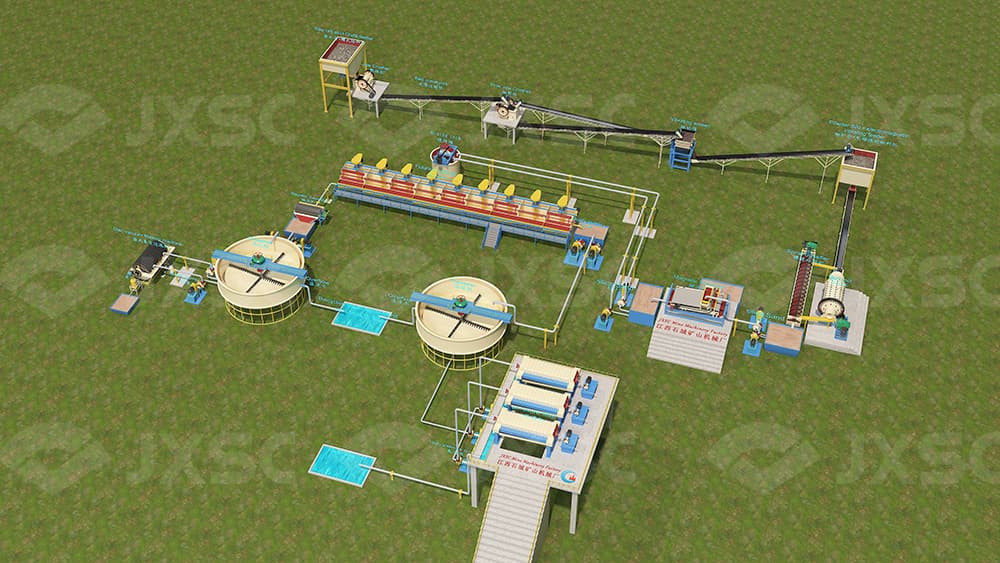
1. Crushing and grinding
Crushing: The mined potassium feldspar ore is screened to remove large pieces of ore (separately processed), and the minerals are processed into suitable particle sizes through one coarse crushing and one or two fine crushing. Jaw crushers and impact crushers are commonly used in the crushing process. During the fine crushing process, a part of the iron-containing ore will be dissociated into monomers. In order to improve the efficiency of the later ore dressing, the finely crushed minerals are passed through a magnetic separator to initially remove the high-iron ore particles.
Grinding: The iron-removed minerals are transported to the grinding closed-loop circulation system by a belt conveyor. The ore particles after grinding can also be further removed by magnetic separators to remove iron-containing minerals.
2. Separation
The separation process often uses flotation, magnetic separation, and other methods to separate quartz, mica, sodium, and other impurities.
(1) Magnetic separation: Magnetic separation is a common method for potassium feldspar beneficiation. It can remove iron minerals, biotite, tourmaline, and other impurities with certain magnetism in feldspar. Magnetic separation is often interspersed in the entire beneficiation process and used in conjunction with other beneficiation methods. The equipment used includes drum magnetic separators, high gradient magnetic separators, etc.;
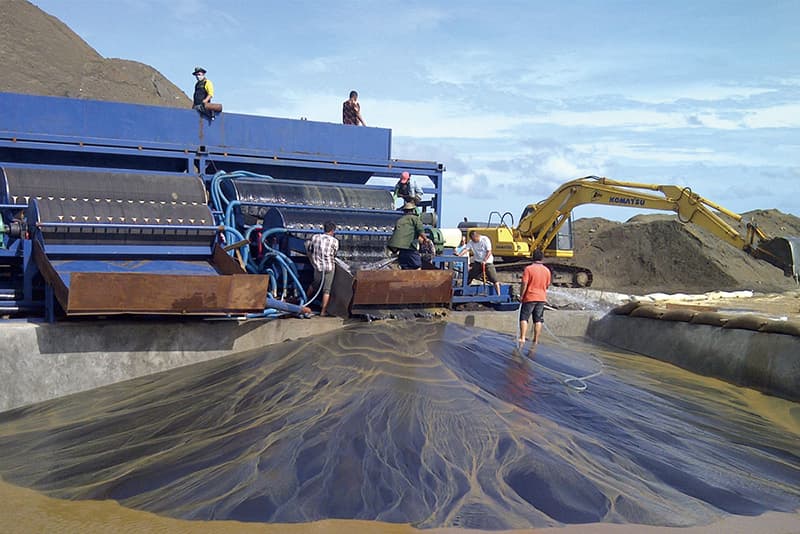

(2) Flotation: The ore powder after iron removal is adjusted into slurry and enters the flotation machine. After adding reagents, flotation is used to remove titanium minerals and non-metallic impurities such as quartz, mica, silicon, and calcium. Commonly used flotation methods include acid flotation, neutral flotation, alkaline flotation, etc., and the equipment used includes flotation machines, stirring tanks, etc.;
(3) Acid leaching: Acid leaching is also an effective way to remove impurities in potassium feldspar. It often uses high-concentration sulfuric acid at high temperatures for a long time to remove iron impurities. It is often suitable for impurities with fine crystalline structures in potassium feldspar.

4. Dehydration operation
After beneficiation, minerals contain a lot of water and need to be dehydrated. In this step, the slurry is first dehydrated by a thickener, and the bottom flow enters a filter (such as a vacuum disc filter) further to reduce the moisture content of the mineral powder. If dry powder is required, a dryer should be added.
JXSC has 38 years of experience in the mining industry, and many experienced engineers provide professional technical support to customers. We focus on providing turnkey solutions and full equipment sales services for mining. Over the years, we have served hundreds of customers at home and abroad. Please send us your mining information. JXSC can provide more accurate suggestions based on your specific situation.




