Lead Zinc Processing Plant
Lead and zinc are closely symbiotic in primary mineral deposits and have significant sulfide affinity. They mainly occur in the form of sulfides. Typical minerals include galena (PbS) and sphalerite (ZnS). Common associated minerals include pyrite, chalcopyrite, and marcasite, while the main gangue minerals include quartz, calcite, barite, etc.
The sulfur-containing nature of lead-zinc ore makes it very suitable for flotation separation methods.
Process Description
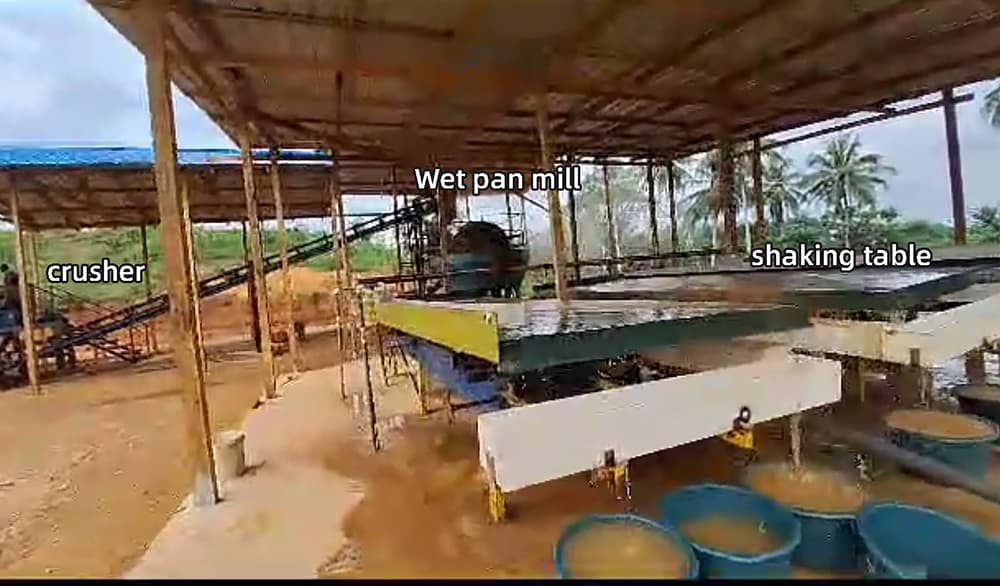
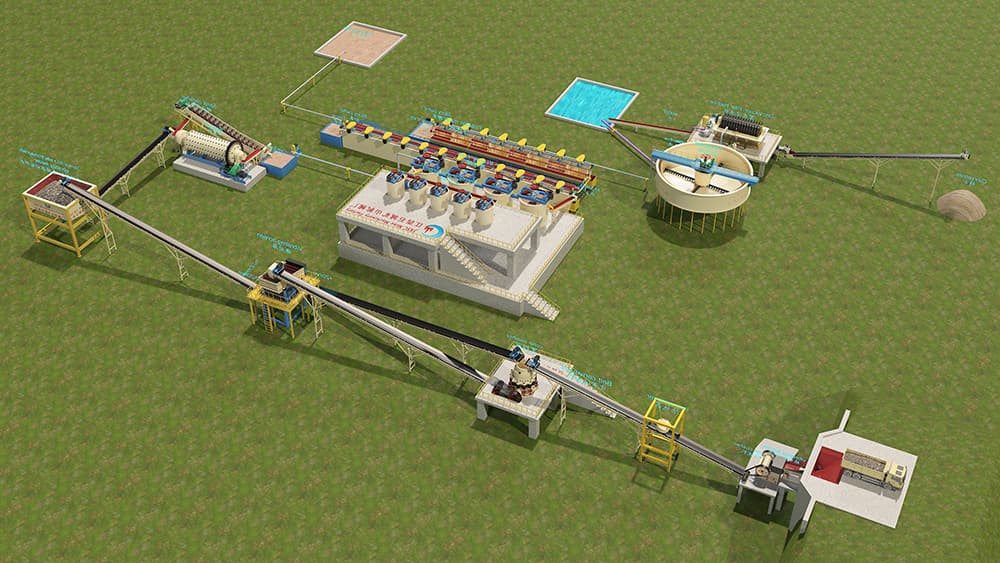
Lead-zinc ore beneficiation mainly uses flotation. The process generally includes four main stages: crushing and screening, grinding, separation and dehydration.
Crushing
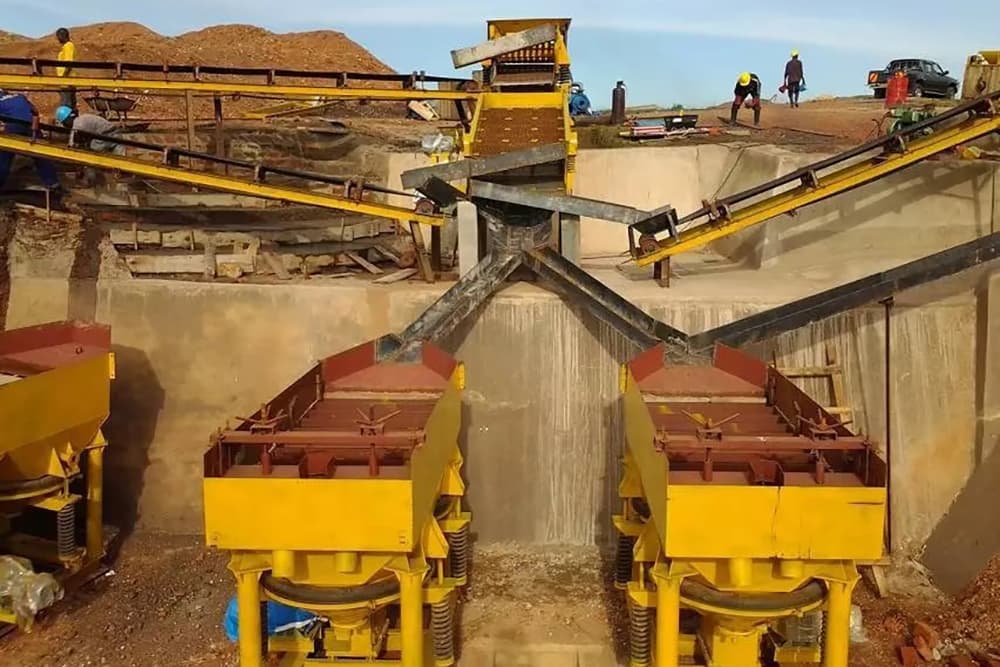
The lead-zinc ore crushing process mainly adopts three processes: two-stage one-closed-circuit crushing, two-stage open-circuit crushing and three-stage one closed-circuit crushing. The selection of specific processes needs to be determined based on the physical properties and mud content of the raw ore. For ores with large mud content, ore needs to be washed to disintegrate the mud clumps before crushing.
Pre-screening is usually set up before crushing operations to separate fine-grained ores and improve crushing efficiency. The crushing process uses a jaw crusher for coarse crushing and a cone crusher for medium and fine crushing. A closed-circuit screening system is set up in the final stage to ensure that the product particle size meets the process requirements.
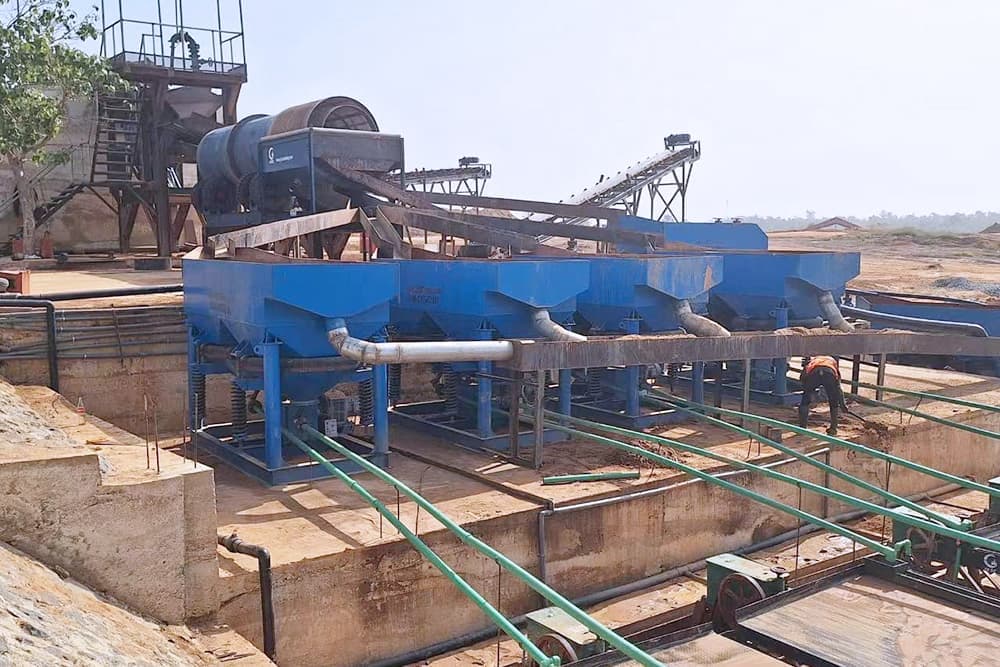
Grinding
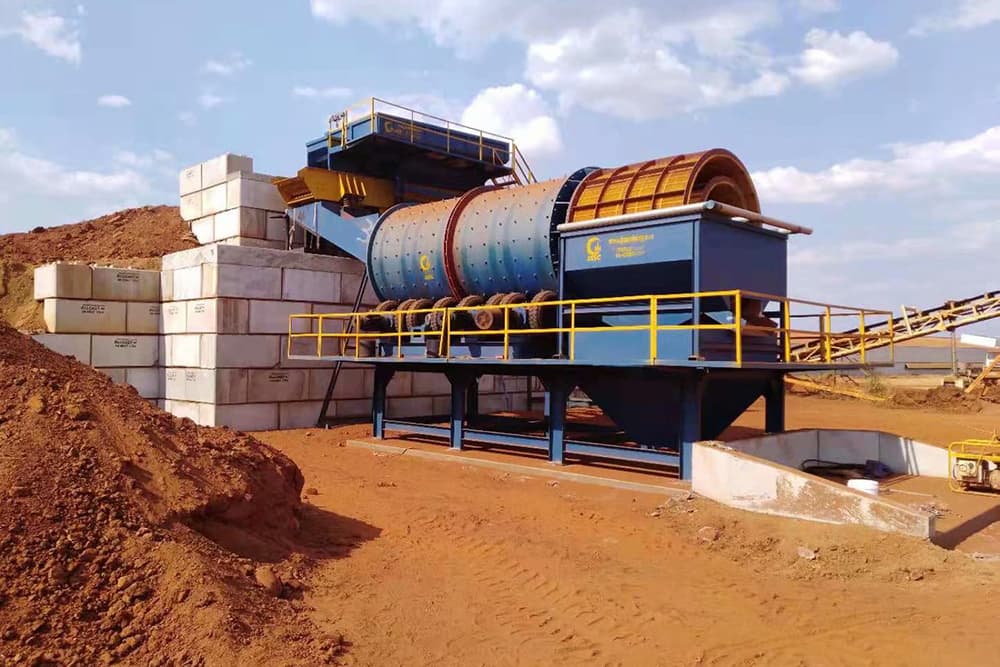
The grinding process is mainly divided into two schemes: “one-stage grinding” and “two-stage grinding”.
The grinding equipment is mainly ball mill, and the spiral classifier cooperates to form closed-circuit grinding. Unqualified particles are returned to the ball mill for regrinding. When the ore dressing scale is large, a two-stage grinding process can be used to improve processing capacity.
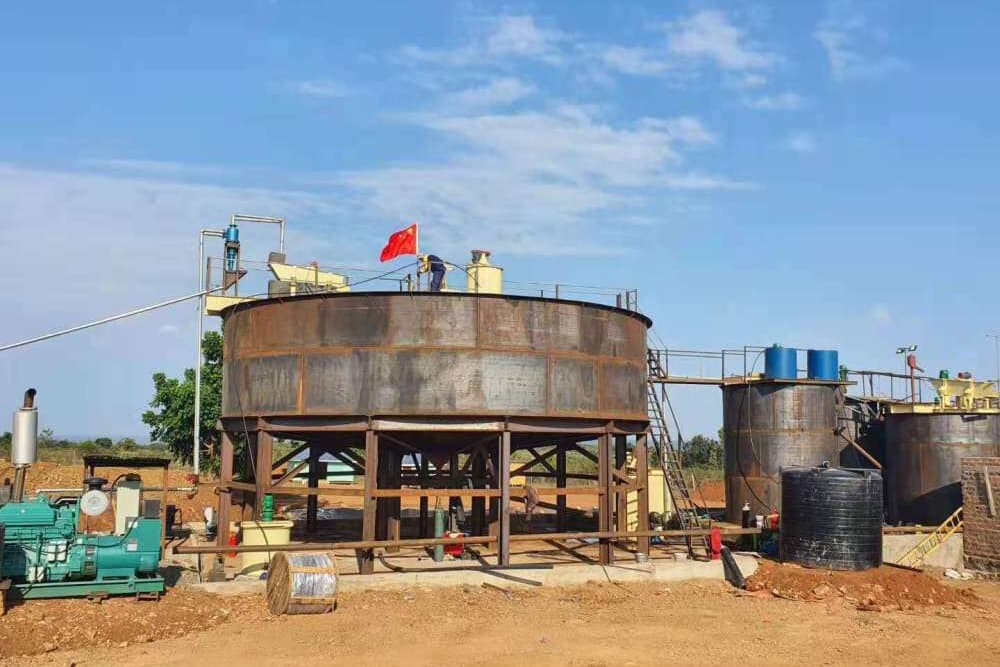
Flotation
The lead-zinc ore flotation process mainly includes the following three types:
Priority flotation process: First add a lead collector to separate the lead concentrate, while suppressing zinc minerals, and then float the remaining minerals to produce zinc concentrate. This process is particularly suitable for ores with a high degree of dissociation of lead and zinc mineral monomers.
Mixed flotation process: By adding lead and zinc co-collectors, lead and zinc mixed concentrates are flotated at one time, and then lead and zinc are separated to obtain respective concentrates. This process is suitable for processing ores with complex embedded patterns and is easy to operate, but it consumes a lot of chemicals and has high operating costs.
Partial priority flotation process: first select lead minerals that are easy to float, then carry out mixed flotation on the tailings, and finally complete the separation of lead and zinc. This process combines the advantages of the first two methods and is suitable for ores with uneven dissociation of lead and zinc minerals, but has a large demand for flotation equipment.
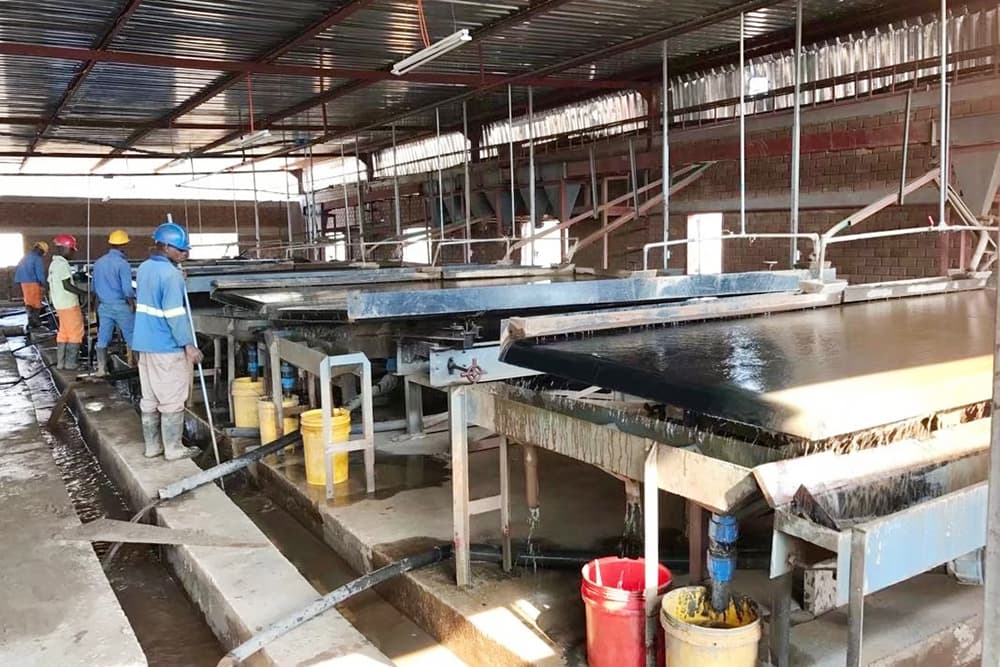
Dehydration
Concentrate dehydration adopts a thickening-filtration process, solid-liquid separation is carried out through a thickener, and then dehydrated by a filter press to form a concentrate cake, and finally the finished concentrate is obtained.