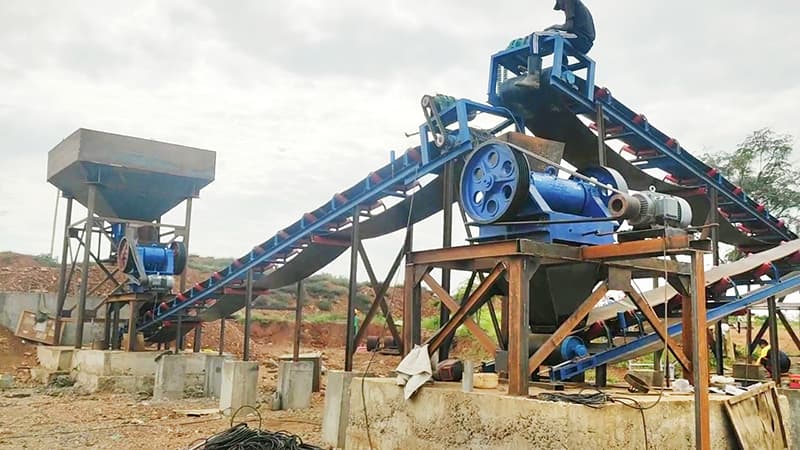

In the mining, construction and material processing industries, crushers play a vital role. Among them, jaw crusher and hammer crusher are the two most common and important crushing equipment. Although they are both used for material crushing, they have significant differences in application scope, working principle and effect. This article will compare the features of these two crushers in detail to help you make a more informed decision when choosing.
The difference in application scope
Jaw crusher is suitable for crushing materials of various hardness:
Hard materials: granite, basalt and other hard rocks.
Medium hardness materials: limestone, marble, etc.
Soft materials: shale, sandstone, etc.
Others: ores, slag, building stones, etc.
Hammer crushers are more focused on specific types of materials:
Brittle materials with medium hardness and below.
Common applications: coal, limestone, gypsum, shale, etc.
Particularly suitable for: cement production, coal preparation plants, coke processing and other industries.
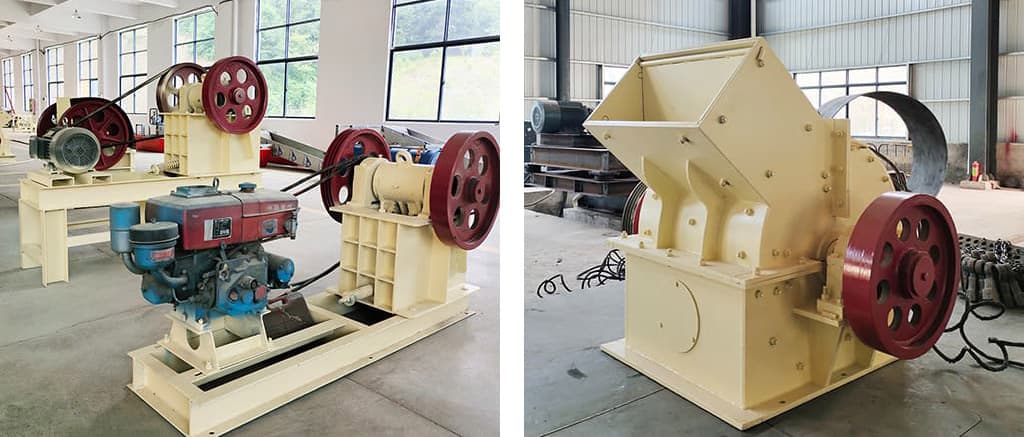

Crushing capacity and product characteristics
The crushing ratio is large, usually 3-7.
Can handle materials with compressive strength not exceeding 350MPa.
Product particle size range: 10-90mm, adjustable.
The product has good particle shape, mainly cubic shape.
Suitable for crushing materials with compressive strength not exceeding 150MPa.
Product particle size is finer: usually ≤10-19mm.
The crushing ratio can reach 40, which is much higher than that of jaw crusher.
The product is in the form of needle sheets and is suitable for applications requiring fine granularity.
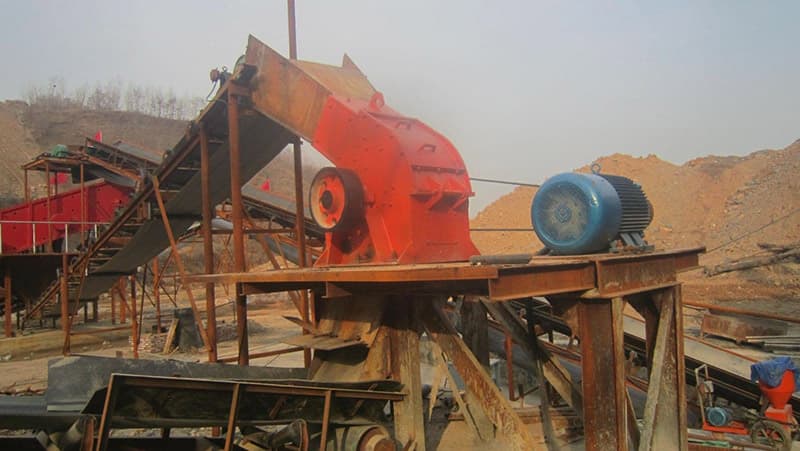
The essential difference in working principles

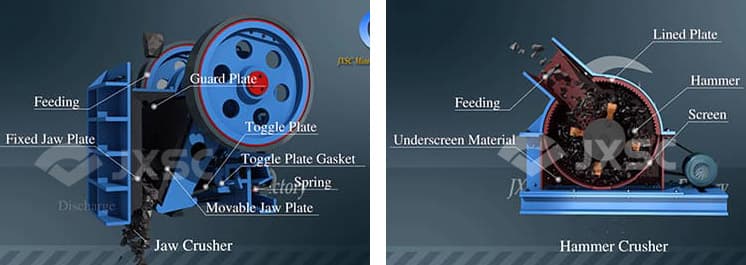
Core components: fixed jaw plate and movable jaw plate.
Working process:
The movable jaw plate performs periodic reciprocating motion.
When the material enters the crushing cavity, it is squeezed, bent and split.
The crushed materials are discharged from the lower part.
Core components: high-speed rotating rotor and hammer.
Working process:
The rotor rotates at high speed and drives the hammer head.
The material is impacted, sheared and torn by the hammer head.
The crushed materials further interact with the screen plate and baffle.
Materials that reach the required particle size are discharged through the sieve plate.
Performance characteristics comparison
| Features | Jaw crusher | Hammer crusher |
| Applicable material hardness | High | Medium-low |
| Product particle size | Coarse to medium | Medium to fine |
| Product particle shape | Good (cubic) | Average (needle-shaped) |
| Production capacity | Medium | High |
| Energy consumption | Low | High |
| Maintenance cost | Low | Medium |
| Noise level | Medium | High |
| Equipment investment | High | Medium |

When processing hard or large-size products, a jaw crusher is a better choice.
When fine-size output is required, or the material is a brittle material with medium or low hardness, a hammer crusher may be more suitable.
For occasions where large capacity is required, hammer crushers can usually provide higher processing capacity.
When considering long-term operating costs, the jaw crusher may have an advantage due to its lower maintenance costs.
In environmentally sensitive areas, the jaw crusher may be a better choice due to its lower noise level.
Ultimately, the choice of crusher should be based on your specific application needs, material characteristics, capacity requirements, and budget.
JXSC has 38 years of experience in the mining industry, and many experienced engineers provide professional technical support to customers. We focus on providing turnkey solutions and full equipment sales services for mining. Over the years, we have served hundreds of customers at home and abroad. Please send us your mining information. JXSC can provide more accurate suggestions based on your specific situation.




